[메타코드 강의 후기] 딥러닝 Deep Learning | Tensor (3)

메타코드?
메타코드는 IT 대기업 현직자 + 서울대/카이스트 AI 박사 등 검증된 강사진들로 구성되어 있으며,
현직자 특강, 커리어 멘토링, 포트폴리오, 공모전, 채용정보 등 실제 취업에 도움이 될 수 있는 양질의 컨텐츠를 제공하고 있습니다.
Tensor Aggregation : min, max, mean
tensor.min()
tensor.min은 텐서의 최소값을 찾는 메서드입니다.
a = torch.tensor([[3,1,4], [2,4,5]]) # 2x3 텐서 생성
print(a) # 텐서 출력
print(a.shape) # 텐서의 차원 출력
print(a.min()) # 텐서 a의 전체 요소 중 최소값 찾기
print(a.min(dim=0)) # 차원 0 (열을 따라)의 최소값 찾기
print(a.min(dim=1)) # 차원 1 (행을 따라)의 최소값 찾기
result: 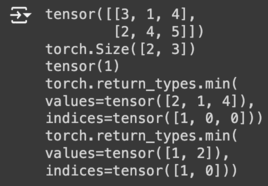
tensor.max()
tensor.max는 텐서의 최댓값을 찾는 메서드입니다.
a = torch.tensor([[3,1,4], [2,4,5]]) # 2x3 텐서 생성
print(a) # 텐서 출력
print(a.shape) # 텐서의 차원 출력
print(a.max()) # 텐서 a의 모든 요소의 최댓값 찾기
print(a.min(dim=0)) # 차원 0 (열을 따라)의 최댓값 찾기
print(a.min(dim=1)) # 차원 1 (행을 따라)의 최댓값 찾기
result: 
tensor.mean()
tensor.mean은 텐서의 평균값을 계산하는 함수입니다. 텐서의 모든 요소의 평균을 반환하거나, 선택적으로 특정 차원을 따라 평균을 계산할 수 있습니다.
a = torch.FloatTensor([[1,2,3], [4,5,6]]) # 2x3의 부동소수점 텐서 생성
print(a) # 텐서 출력
print(a.mean()) # 텐서 a의 전체 요소 중 평균값 계산
print(a.mean(dim=0)) # 차원 0 (열을 따라)의 평균값 출력
print(a.mean(dim=1)) # 차원 1 (행을 따라)의 평균값 출력
result: 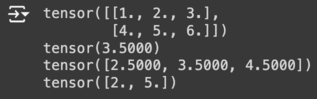
Shaping Operation : reshape, squeeze/unsqueeze, stack, cat
tensor.reshape()
tensor.reshape은 텐서의 형태(차원)를 변경하는 데 사용됩니다. 이 함수는 텐서의 데이터를 유지하면서 새로운 형태로 재배열합니다. 주의: 새로운 형태가 원본 텐서의 요소 수와 정확히 일치해야 합니다.
# 2x4 텐서 생성
a = torch.tensor([[1,2,3,4], [5,6,7,8]])
# 텐서의 형태 출력
print(a.shape)
# 텐서 출력
print(a)
# 2x4 텐서를 4x2 텐서로 변경
print(a.reshape([4,2]))
# 2x4 텐서를 1x2x4 텐서로 변경
print(a.reshape([1,2,4]))
# 2x4 텐서를 2x2x2 텐서로 변경
print(a.reshape([2,2,2]))
# 2x4 텐서를 크기가 4인 두 개의 차원으로 변경
print(a.reshape([-1, 4]))
# 위 변경된 텐서의 형태 출력
print(a.reshape([-1, 4]).shape)
# 2x4 텐서를 3x4 텐서로 변경하려 시도
print(a.reshape([3,4])) # 에러 발생
result: 
마지막 코드에서 에러가 발생하는 이유는, 텐서의 형태를 변경할 때 요소의 총 수가 변경 전과 변경 후에 일치해야 한다는 기본 규칙을 위반했기 때문입니다.
reshape()는 새로운 형태가 원본 텐서의 요소 수와 정확히 일치해야 합니다. 예를 들어, 12개의 요소를 가진 텐서는 3x4, 2x2x3 등 12를 요소 수로 나눌 수 있는 차원으로만 변경할 수 있습니다.
tensor.squeeze()
tensor.squeeze는 크기가 1인 차원을 제거하는 데 사용됩니다. 이 함수는 주로 데이터의 차원을 정리하거나 불필요한 싱글톤 차원을 제거하여 텐서의 구조를 단순화하는 데 유용합니다.
# 크기가 1인 차원을 포함하는 텐서 생성
tensor = torch.zeros(2, 1, 2, 1, 2)
print("Original tensor shape:", tensor.shape)
# 모든 크기가 1인 차원을 제거
squeezed_tensor = tensor.squeeze()
print("Tensor shape after squeeze():", squeezed_tensor.shape)
# 특정 차원을 지정하여 squeeze
squeezed_dim_tensor = tensor.squeeze(1)
print("Tensor shape after squeeze(1):", squeezed_dim_tensor.shape)
# 크기가 1이 아닌 차원을 squeeze
squeezed_non_one_dim_tensor = tensor.squeeze(0)
print("Tensor shape after squeeze(0):", squeezed_non_one_dim_tensor.shape) # No change
result: 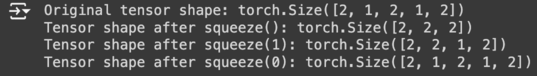
squeeze() 함수는 뷰(view)를 반환할 수 있으므로, 반환된 텐서를 수정하면 원본 텐서에도 영향을 줄 수 있습니다.
뷰 대신 실제 데이터 복사본을 생성하고 싶다면 clone()을 사용한 후에 squeeze()를 호출할 수 있습니다.
tensor.unsqueeze()
tensor.unsqueeze는 텐서에 새로운 차원을 추가하는 데 사용됩니다. 이 함수는 지정된 위치에 차원을 추가하여 텐서의 형태를 변경하며, 특히 다차원 배열을 다룰 때 데이터의 구조를 조작하는 데 유용합니다.
# 원본 텐서 생성
tensor = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3, 4])
print("Original tensor shape:", tensor.shape)
# 차원을 추가하여 1x4 텐서 생성
unsqueeze_tensor = tensor.unsqueeze(0)
print("Tensor shape after unsqueeze(0):", unsqueeze_tensor.shape)
# 차원을 추가하여 4x1 텐서 생성
unsqueeze_tensor_2 = tensor.unsqueeze(1)
print("Tensor shape after unsqueeze(1):", unsqueeze_tensor_2.shape)
result: 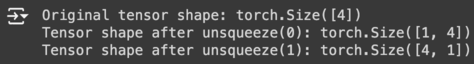
unsqueeze()는 뷰를 반환할 수 있으므로 반환된 텐서를 수정하면 원본 텐서에도 영향을 줄 수 있습니다.
필요한 경우 clone()을 사용하여 뷰가 아닌 데이터 복사본을 작업할 수 있습니다.
unsqueeze()의 dim 파라미터는 음수 값을 사용할 수도 있는데, 이 경우 텐서의 끝에서부터 차원을 추가합니다.
예를 들어, -1은 텐서의 마지막에 차원을 추가합니다.
torch.cat()
여러 텐서를 지정된 차원을 따라 연결(concatenate)하는 데 사용됩니다. 이 함수는 데이터를 병합할 때 유용하며, 딥러닝에서는 특히 다양한 네트워크 레이어의 출력을 결합할 때 많이 사용됩니다.
torch.cat(tensors, dim=0)에서 tensors는 연결하고자 하는 텐서의 리스트나 튜플이며, dim은 연결할 차원을 지정합니다.
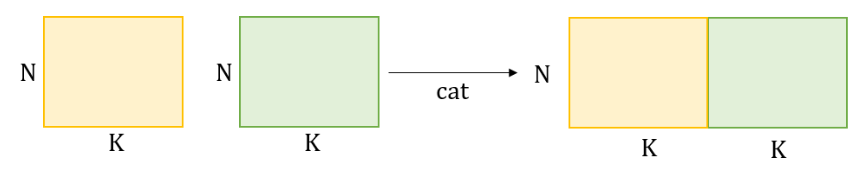
a = torch.rand(5, 24, 50) # [M, N, K]
b = torch.rand(5, 24, 50) # [M, N, K]
output1 = torch.cat([a, b], dim=0) # [M+M, N, K]
print(output1.shape)
output2 = torch.cat([a, b], dim=1) # [M, N+N, K]
print(output2.shape)
output3 = torch.cat([a, b], dim=2) # [M, N, K+K]
print(output3.shape)
result: 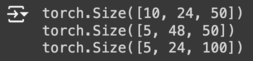
a = torch.rand(5, 24, 50)
b = torch.rand(2, 24, 50)
output1 = torch.cat([a, b], dim=0)
print(output1.shape)
output2 = torch.cat([a, b], dim=1)
print(output2.shape)
result: 
output2 = torch.cat([a, b], dim=1)에서 에러가 발생하는 이유는
torch.cat() 함수를 사용할 때, 연결하려는 텐서들이 지정된 차원(dim=1인 경우)을 제외한 모든 다른 차원에서 크기가 동일해야 하기 때문입니다.
torch.stack()
torch.stack은 여러 텐서를 새로운 차원을 추가하면서 쌓는(stacking) 데 사용됩니다. 이 함수는 torch.cat()과 유사하지만, stack은 모든 입력 텐서들 사이에 새로운 차원을 추가하는 차이가 있습니다. 이는 텐서들이 같은 모양을 가지고 있을 때만 사용할 수 있습니다.
torch.stack(tensors, dim=0)에서 tensors는 쌓고자 하는 텐서의 리스트나 튜플이며, dim은 새로운 차원을 삽입할 위치를 지정합니다.
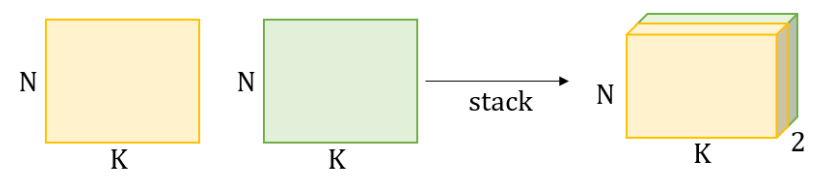
a = torch.rand(3, 4, 2) # [M, N, K]
b = torch.rand(3, 4, 2) # [M, N, K]
output = torch.stack([a, b], dim=3)
print(output.shape)
print(output)
result: 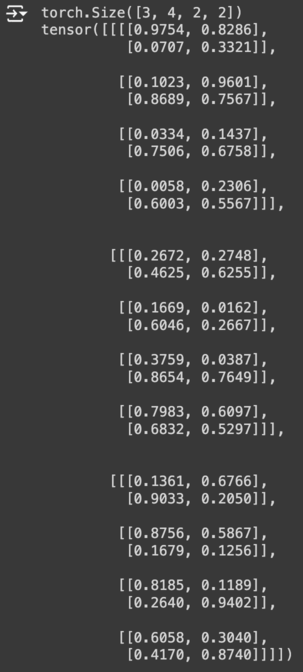
이런 분들께 추천합니다!
서포터즈 강의료 지원을 받아 작성하였습니다